Whether you use SSDs, HDDs, or any type of hardware RAID array for your server, you need a disk management tool to help manage storage devices. Windows Server 2012 R2 includes a native "Disk Management" tool that can help you create, delete, format partitions, set partitions as Active, and change drive letters and paths. Although it has partition resizing capabilities, it cannot extend a partition by shrinking another one. If you want to resize partitions without limitations or need additional features, such as merging, copying, converting, or wiping partitions, you will need disk partition software. This article explains how to open Disk Management in Windows Server 2012 R2, what it can do, and its limitations compared to disk partition software.

How to open Disk Management in Windows Server 2012
There are 2 ways to open Disk Management in Windows Server 2012 R2:
- Press Windows + X on the keyboard and click Disk Management in the list.
- Press Windows + R on the keyboard, type diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.
The ability of Windows Server 2012 Disk Management tool
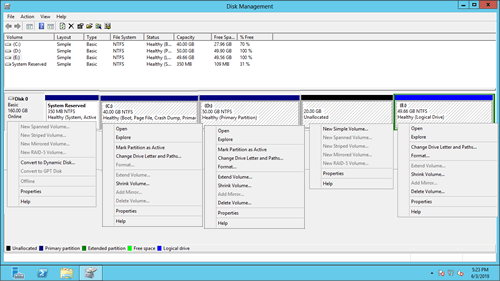
"Disk Management" is a Microsoft Windows built-in utility first introduced in Windows XP. It has similar ability with Diskpart command but work with a graphical interface. It displays all connecting hard disk with layout on bottom, it also lists all single partitions on the top followed by the type, file system, status, capacity, free space, usage percentage, etc.
It enables users to view and manage the disk drives installed in their computer and the partitions associated with those drives. Windows Server 2008 improved the ability by adding new "Shrink Volume" and "Extend Volume" functions. Windows Server 2012 inherited the same interface and functions without any improvement.
What does Windows Server 2012 Disk Management do:
To a brand new hard disk:
Online, offline and initialize. Hard disk must be online and initialized before creating new volume. When initialize disk, you can select partition style as MBR or GPT.
To Unallocated space:
Create one or more new volumes.
To a disk with volume:
Convert basic disk to Dynamic disk.
To a disk without any volume:
Convert MBR disk to GPT and vice versa, convert basic disk to Dynamic disk and vice versa.
To an allocated partition:
- Open root directory with File Explorer
- Mark partition as Active
- Change drive letter and path
- Format partition
- Shrink volume and make Unallocated space on the right.
- Extend volume with Unallocated space behind it.
- Delete partition
- Add mirror
If you select Add Mirror, both disks will be converted to dynamic.
To dynamic disks:
Disk Management can create Simple, Mirrored, Spanned, Stripped and RAID-5 volume.
To create RAID 5 volume, there must be at least 3 dynamic disks. There are only two in my computer, so this option is grayed out.
Though Windows Disk Management has this ability, but it is not suggested to use dynamic disk volumes, because:
- It uses much resources of this computer and degrade performance.
- Many software do not support dynamic disk volumes.
- Hard disk and RAID controller are much cheaper now.
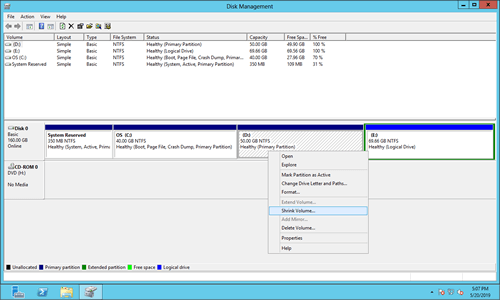
How to shrink partition with Disk Management in Server 2012
One of the useful feature of Disk Management is "Shrink Volume", which is able to decrease allocated partition without losing data. Unallocated space released from this partition can be used to create new volume.
- Press Windows and X on the keyboard, click "Disk Management" in the list.
- Right click a partition (such as D:) and select "Shrink Volume".
- Enter an amount of space and click "Shrink" in the pop-up window.
Note:
- Only NTFS partition is supported.
- Unallocated space can only be made on the right when shrinking a partition.
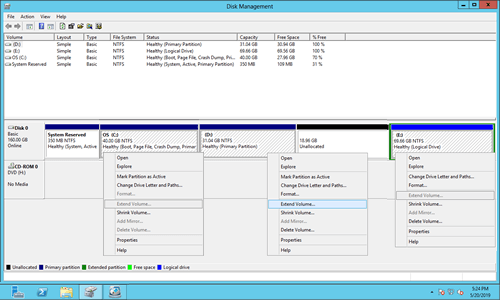
How to extend partition with Server 2012 Disk Management
- Right click the partition that has adjacent unallocated space on the right, and then select "Extend Volume".
- Simply click Next till Finish in the pop-up "Extend Volume Wizard" window.
Note:
- Only NTFS partitions are supported.
- Extend Volume function only works when there's contiguous unallocated space on the right. You cannot get such required space by shrinking other volume in Disk Management. This is the reason why many people feedback that Extend Volume greyed out in Server 2012 after shrinking partition.
Disadvantages of Windows Server 2012 Disk Management
Comparing with Windows Server 2012 native Disk Management tool, NIUBI Partition Editor has more advantages while resizing disk partitions:
- It can shrink and extend both NTFS and FAT32 partitions.
- It can make unallocated space on either left or right when shrinking a volume.
- It can merge unallocated space to either contiguous partition by 1 step.
- It can move and merge unallocated space to any non-adjacent partitions.
- It can merge 2 contiguous partitions in one step.
Besides shrinking and extending partition, NIUBI Partition Editor helps do much more disk/partition management operations in Windows Server 2012, 2016, 2019, 2022, 2025 and previous Server 2003/2008.
What does NIUBI Partition Editor do?
To Unallocated space:
- Create one or more volumes
- Wipe data in it
- Surface test (scan bad sectors)
- View properties (detailed parameters)
To whole disk:
- Initialize
- Change status to offline or online
- Set read-only attribute
- Wipe disk (cannot be recovered)
- Surface test
- View properties
- Clone disk to migrate data and OS
- Convert MBR disk to GPT
- Delete all partitions
- Cleanup disk
To single partition:
- Resize volume (shrink and extend)
- Move location
- Merge two adjacent volumes by 1 step
- Copy partition fastly
- Convert to Logical or Primary partition
- Optimize file system
- Convert NTFS to FAT32
- Change drive letter (such as D:)
- Change label (add a name or modify)
- Set as Active
- Check file system integrity
- Defrag to improve performance
- Hide from File Explorer
- Delete (files can be recovered)
- Format volume to use as new
- Wipe (erase data permanently)
- Surface test
- Explore (view files/folders with directory)
- View properties
Compared to other disk management tool for Windows 2012 server, NIUBI Partition Editor is much safer and faster because of its powerful technologies:
- Virtual Mode: To prevent mistakes, all operations are listed as pending for preview. Real disk partitions are not changed until you click "Apply" to confirm.
- Cancel-at-will: If you apply incorrect operations, you can cancel ongoing tasks without worrying about partition damage.
- 1 Second Rollback: If any error is detected while resizing partitions, the software can automatically revert the server to its original state in an instant.
- Hot Clone: Clone disk partitions without interrupting the server. You can clone the system disk before making changes or as part of a regular backup routine.
- Advanced File-Moving Algorithm: Resize and move partitions 30% to 300% faster, saving significant time, especially when handling a large number of files.